XaaS (Anything as a Service)
XaaS (Everything-as-a-Service)
An extensive number of modern digital services, products and tools are ordered over the internet and delivered to users on demand, rather than provided via local channels within enterprises or specialized organizations. Everything-as-a-Service is a term for services and applications that users can access on the Internet upon request.
What are the benefits of XaaS?
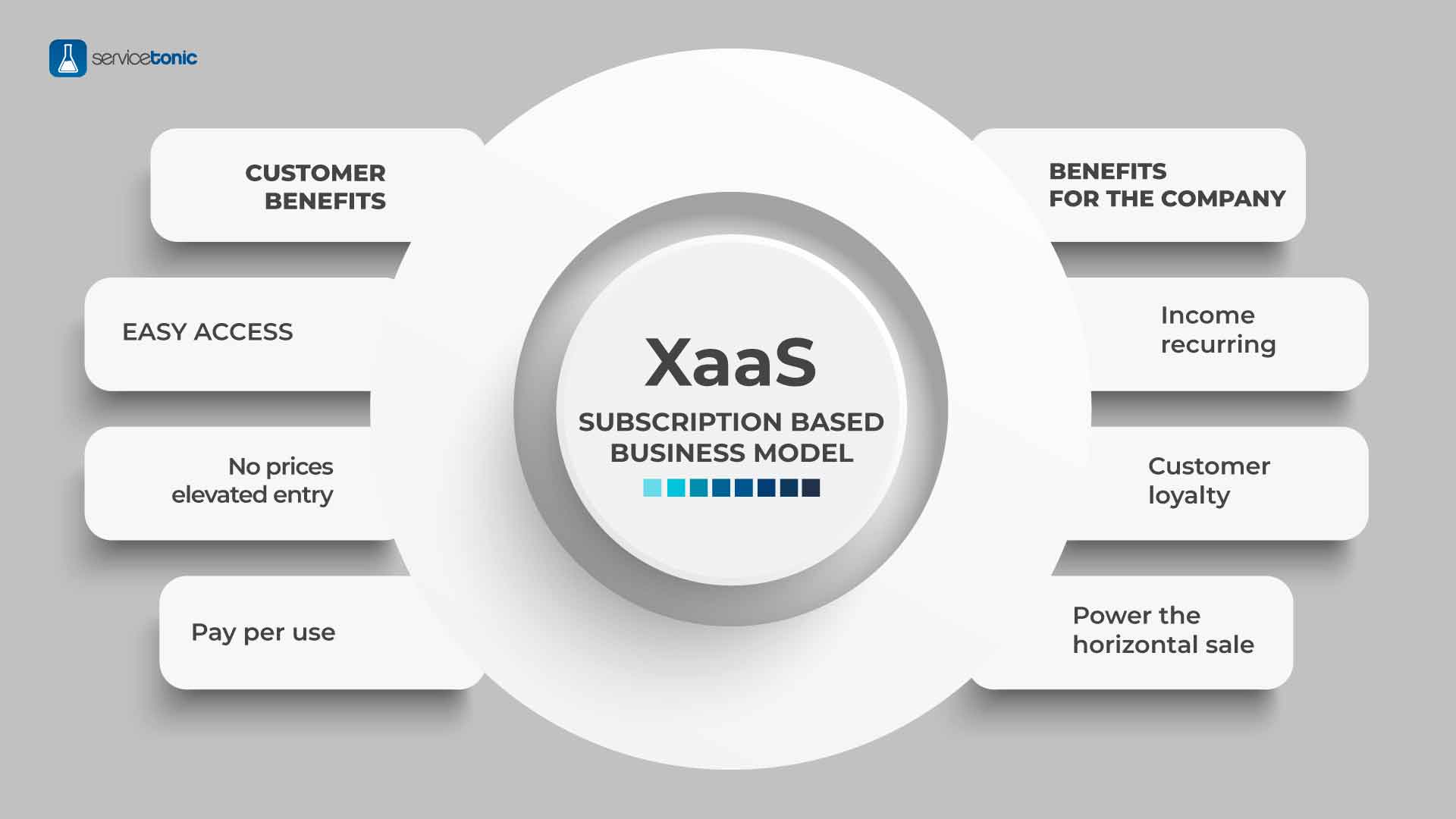
There are several benefits of XaaS: improving the expense model, speeding new apps and business processes, and shifting IT resources to higher-value projects.
Improving the expense model. With XaaS, businesses can cut costs by purchasing services from providers on a subscription basis. Before XaaS and cloud services, businesses had to buy individual products—software, hardware, servers, security, infrastructure—install them on site, and then link everything together to create networks. Now, with XaaS, businesses simply buy what they need, and pay as they go. Previous capital expenses now become operating expenses.
Speeding new apps and business processes. This model allows businesses to quickly adapt to changing market conditions with new apps or solutions. Using multitenant approaches, cloud services can provide much-needed flexibility. Resource pooling and rapid elasticity support mean that business leaders can simply add or subtract services as needed. A company can quickly access new technologies, scaling infrastructure automatically when users need innovative resources.
Shifting IT resources to higher-value projects. Increasingly, IT organizations are turning to an XaaS delivery model to streamline operations and free up resources for innovation. They are also using the benefits of XaaS to transform digitally and become more agile. In a recent survey by Deloitte, 71% of companies report that XaaS now constitutes more than half of their company’s enterprise IT. XaaS provides more users with access to cutting-edge technology, democratizing innovation.
What are some examples of XaaS?
Because XaaS stands for “anything as a service,” the list of examples is endless. Many kinds of IT resources or services are now delivered this way. Broadly speaking, there are three categories of cloud computing models: software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). Outside these categories, there are other examples such as disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS), communications as a service (CaaS), network as a service (NaaS), database as a service (DBaaS), storage as a service (STaaS), desktop as a service (DaaS), and monitoring as a service (MaaS). Other emerging industry examples include marketing as a service and healthcare as a service.
NetApp and XaaS
NetApp provides several XaaS options, including IaaS, IT as a service (ITaaS), STaaS, and PaaS.
IaaS. When you differentiate your hosted and managed infrastructure services, you can increase service and platform revenue, improve customer satisfaction, and turn IaaS into a profit center. You can also take advantage of new opportunities to differentiate and expand services and platform revenue, including delivering more performance and predictability from your IaaS services. Plus, NetApp® technology can enable you to offer a competitive advantage to your customers and reduce time to market for deploying IaaS solutions.
ITaaS. When your data center is in a private cloud, it takes advantage of cloud features to deliver ITaaS to internal business users. A private cloud offers characteristics similar to the public cloud but is designed for use by a single organization. These characteristics include:
-
Catalog-based, on-demand service delivery
-
Automated scalability and service elasticity
-
Multitenancy with shared resource pools
-
Metering with utility-style operating expense models
-
Software-defined, centrally managed infrastructure
-
Self-service lifecycle management of services
STaaS. NetApp facilitates private storage as a service in a pay-as-you-go model by partnering with various vendors, including Arrow Electronics, HPE ASE, BriteSky, DARZ, DataLink, Faction, Forsythe, Node4, Proact, Solvinity, Synoptek, and 1901 Group. NetApp also seamlessly integrates with all major cloud service providers including AWS, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
PaaS. NetApp PaaS solutions help simplify a customer’s application development cycle. Our storage technologies support PaaS platforms to:
-
Reduce application development complexity.
-
Provide high-availability infrastructure.
-
Support native multitenancy.
-
Deliver webscale storage.

